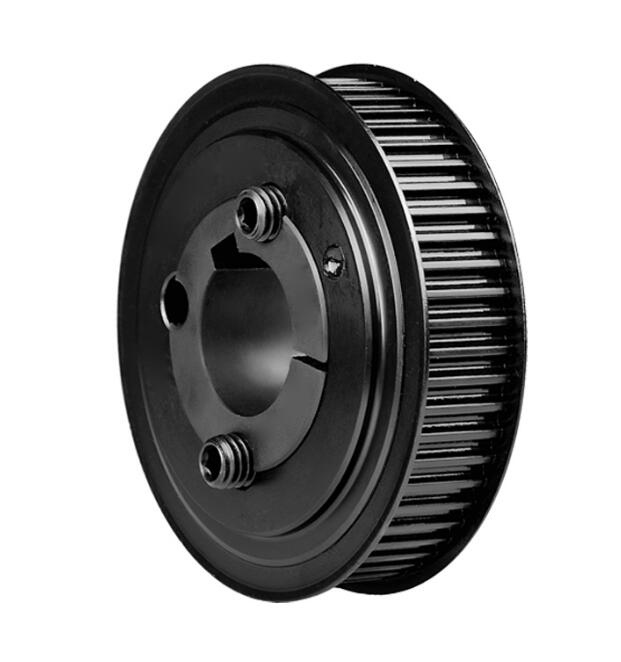
Timing Pulleys
Timing Pulleys
A timing pulley is a type of pulley used in mechanical systems that operate with timing belts to transmit power and motion. These pulleys are typically used in applications where precise timing and synchronization of the rotation are important, such as in engines, conveyor systems, or automated machinery.
Key Features of Timing Pulleys:
- Teeth Design: Timing pulleys have teeth on their circumference that mesh with the teeth of a timing belt. This provides a positive engagement, preventing slippage, and ensures that the driven part of the system rotates in sync with the driver.
- Material: They are often made from materials like aluminium, steel, or plastic, depending on the application and load requirements.
- Types of Timing Pulleys:
- Standard pulleys: Used in most industrial and mechanical applications.
- Idler pulleys: Used to guide the timing belt and maintain proper tension.
- Flanged pulleys: Have raised edges to keep the timing belt from slipping off.
- Applications:
- Automotive engines: For synchronizing the camshaft and crankshaft in timing systems.
- Robotics and CNC machinery: For precise motion control.
- Conveyor systems: For synchronized belt movement.
- Tooth Profiles:
- The most common tooth profiles are ** trapezoidal** and round (also known as curvilinear). These profiles ensure the efficient and smooth engagement between the belt and pulley.
- The most commonly used standards for timing belts and pulleys include GT (Gates Tooth), T series, HTD (High Torque Drive), and STO (synchronous toothed) systems.
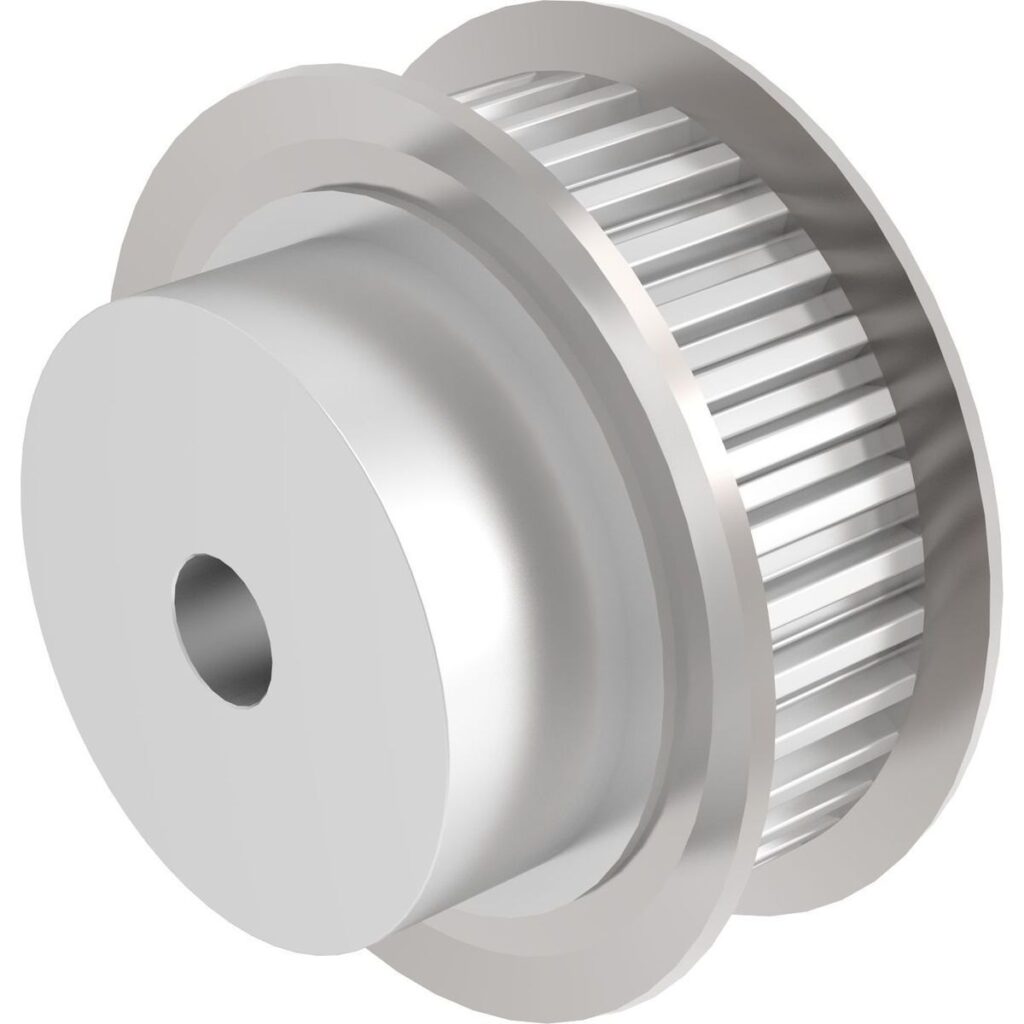

How They Work:
- The teeth on the pulley and timing belt fit together, creating a system that transfers torque efficiently and precisely.
- The meshing of teeth eliminates slippage, making timing pulleys ideal for applications that require synchronized motion or precise speed control.