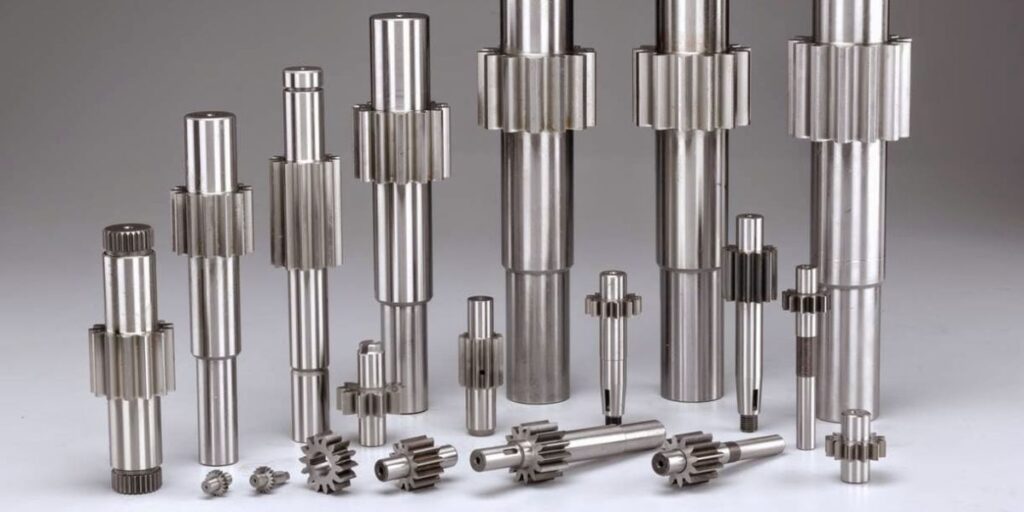
Shafts
MACHINED SHAFTS
We manufacture machined shafts, typically cylindrical in shape, that has been specifically fabricated and shaped through machining processes such as turning, milling, grinding, or drilling. These shafts are commonly used in a wide range of industrial applications, including machinery, automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing, where precise mechanical movement or power transmission is required.
Key Characteristics of Machined Shafts:
- Material: Machined shafts can be made from a variety of materials, such as steel, stainless steel, aluminum, brass, or other alloys. The choice of material depends on factors like strength, corrosion resistance, and weight requirements.
- Precision: Machining processes ensure high precision in the shaft’s dimensions and surface finish. This is critical in ensuring that the shaft fits correctly within its assembly and operates smoothly.
- Surface Finish: The surface finish of a machined shaft is often highly polished or ground to reduce friction and wear during operation, improving performance and extending the lifespan of the shaft.
- Custom Shapes and Sizes: While shafts are typically cylindrical, they can also be made with keyways, grooves, threads, or splines, depending on the application. Custom designs are often required to fit specific machines or mechanisms.
- Load-Bearing: Machined shafts are designed to transmit torque and rotational power, making them crucial in gear systems, motors, and other mechanical assemblies. They are often subjected to high loads and rotational forces.
SHAFTS in alloy steel, stainless steel up to 3meter length & 500mm diameter duly machined, hard chrome plated & ground finish.

Common Machining Processes Used:
- Turning: A lathe machine is used to rotate the shaft while a cutting tool removes material to achieve the desired shape and size.
- Grinding: Fine grinding processes can be used to achieve a high-quality surface finish and precise diameter.
- Milling: For creating more complex profiles or features on the shaft, such as grooves or slots.
- Drilling & Boring: For creating holes for shafts or to make internal features like bearings or lubrication channels.
Applications of Machined Shafts:
- Power Transmission: In motors, engines, and gearboxes, machined shafts transfer power between components.
- Automotive: Driveshafts, axles, and crankshafts are machined to specific tolerances to ensure they function effectively in vehicles.
- Aerospace: Shafts in turbine engines and other components require high precision and durability to withstand extreme operating conditions.
- Industrial Machinery: Shafts in conveyor systems, pumps, and other machines rely on machined shafts to function with precision and durability.